
The above-mentioned Google Trends graph indicates :
(i) Blue colour line – The number of times the term “How to register a company in India” has been searched over the past 12 months in India
(ii) Red colour line – The number of times the term “How to start a business in India” has been searched over the past 12 months in India
Starting a business may seem like a challenging proposition, especially if you do not know where to begin. When you embark on your journey as an entrepreneur, it is important to understand the basic steps.
CONTENT :
- What is a company?
- What are the different types of companies?
- How to register a company in India?
1. WHAT IS A COMPANY
A company is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared goals. A company can be created as a legal person so that the company itself has limited liability as members perform or fail to discharge their duty according to the publicly declared incorporation, or published policy. When a company closes, it may need to be liquidated to avoid further legal obligations.
In simpler words, a company is a voluntary association of an individual or a group of individuals, recognized by law, to carry on the business for profit, despite factors such as death, bankruptcy, insanity, change in membership etc. A company makes or promotes goods and services, and recruits’ employees to achieve the company’s goals and objectives.

For example:

Tata Consultancy Services is an Indian multinational technology company that specializes in information technology services and consulting, headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
2. WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF COMPANIES?
Deciding on the right type of company is very crucial. This decision would impact various factors such as process, taxes and scope of work.

Below mentioned are the conventional classification of the companies in India which are defined under the CA of 2013. There is the 4+1 broad classification of companies:
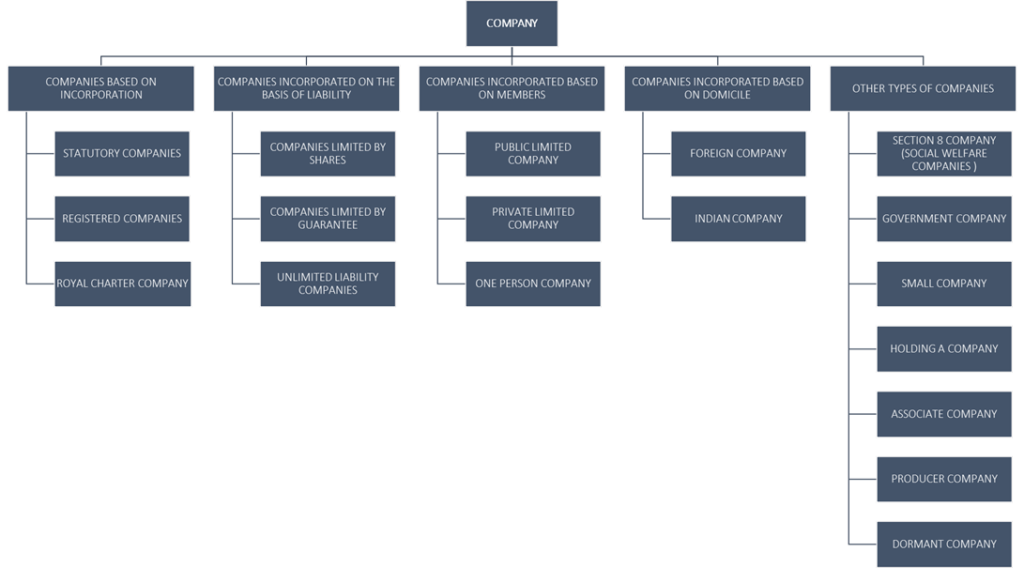
COMPANIES BASED ON INCORPORATION
The incorporation of a company refers to the legal process that is used to form a corporate entity or a company. An incorporated company is a separate legal entity on its own, recognized by the law.
Under this category, there are THREE such companies :
| STATUTORY COMPANIES | These are companies that a Special Act of the Parliament forms and it provides services of value to the public. Example: Air India, State Bank of India, LIC |
| REGISTERED COMPANIES | These are companies which are registered under the statute of the Companies Act. All companies in India are registered in the CA of 2013. Example: Flipkart, Myntra, Urban Company |
| ROYAL CHARTER COMPANIES | These are companies which are born from the authorization of the sovereign or the crown. Example: East India Company |
COMPANIES INCORPORATED ON THE BASIS OF LIABILITY
Under this category there are THREE such companies:
| COMPANIES LIMITED BY SHARES: | In such companies, its members are liable to the creditors of the company based on the unpaid shares held by them which are under Section 2(22) of CA of 2013. These companies provide their shareholders with limited liability in the event a company winds up. In the USA, such companies are called “Inc.” Example: Reliance Industries |
| COMPANIES LIMITED BY GUARANTEE: | In such companies, its members/shareholders will be liable to pay the creditors an amount that they would undertake to contribute when a company winds up. Such companies are referred to as “not for profit” or “charitable companies” where the members decide not to withdraw the profit that accrues but redeploy the accrued profits for the good of the business. Example: Tata Trusts |
| UNLIMITED LIABILITY COMPANIES: | In such companies, its shareholders will need to compensate the creditors in proportion to the interests that they hold in the company which means business owners are personally liable for any loss the business makes. An apt example is a sole trader and partnership firms who need to compensate their creditors based on their business debts. |
COMPANIES INCORPORATED BASED ON THE MEMBERS
Under this category there are THREE such companies:
| PUBLIC COMPANY | A public limited company or called a publicly-traded company is where the shares can be bought/sold by the public in a stock exchange. Most companies in India that are listed in the National Stock Exchanges are publicly traded. Example: Bharat Petroleum |
| PRIVATE COMPANY | A private company is where the articles of the company would prevent its members from transferring their shares to others. Also, this limits the number of members between 2 and 200 only. Example: Lifestyle |
| ONE PERSON COMPANY (OPC): | This is one of the new enactments passed under the CA of 2013 wherein a company can be formed by one person, unlike other companies which requires a minimum of 2 people to form a company. If you are looking to have full control and manage sole ownership, OPC would be right for you. Example: Truffles |

Please note :
Based on the budgetary speech on 1st February 2021, the Government of India has incentivized OPC which allows such companies to grow without the restriction of paid-up capital and turnover, secondly allowing an OPC to convert to any other company, third an Indian citizen can set up an OPC within 120 days instead of 182 days and finally an NRI can set up an OPC
COMPANIES INCORPORATED BASED ON DOMICILE
| FOREIGN COMPANY | A foreign company is a company that is incorporated outside India but has a place of business in India by itself physically or through an agent or through an electronic mode. This company conducts business activity in India. Example: ABB, Abbot |
| INDIAN COMPANY | This is a company that is formed and registered in India. Example: HDFC Bank |
OTHER TYPE OF COMPANIES
Under this category there are EIGHT such companies:
| SECTION 8 COMPANY (SOCIAL WELFARE COMPANIES) | The main purpose of incorporating a company under Section 8 of the CA of 2013 is to promote social welfare. The objective of forming such a company is to promote commerce, art, science, sports, education, research, social welfare, religion, charity. Such companies can redeploy their profits to fulfil their objectives. Example: Reliance Foundation |
| GOVERNMENT COMPANY | In a Government Company, 51% of their paid-up capital is held by the Central Government or by a State Government. Being a Government Company, these companies enjoy certain privileges and exemption under the Companies Act. Example: HMT – Hindustan Machine Tools Limited |
| SMALL COMPANY | It’s a company where the paid-up capital does not exceed 50 lakh rupees or a prescribed amount of not greater than 10 crore rupees. However, the turnover from such companies should not exceed 2 crore rupees or a prescribed amount that should not exceed 100 crore rupees. Example: Malabar Gold & Diamonds |
| SUBSIDIARY COMPANY | A subsidiary company wherein the parent company controls the composition of directors of the company and exercise more than half of the voting power. Example : Tata has a strong global network of 134 subsidiaries, associate companies and joint ventures, including the Jaguar Land Rover in the UK and the Tata Daewoo in South Korea. Tata Motors Group is the Largest Tata Group Subsidiary based on the Turnover. |
| HOLDING COMPANY | As per Section (2) of the CA of 2013, a holding company is a company that holds other companies as subsidiaries. An apt example is the company Alphabet that owns Google, YouTube, Nest. These holding companies are conglomerates that own several unconnected businesses. |
| ASSOCIATE COMPANY | An associate company is in which another company has “significant influence” on the other company, but the company is not a subsidiary company. For example, the company Pidilite Industries Limited which manufactures the product Fevicol has Vinyl Chemicals (India) Limited as its Associate Company. However, the term “significant influence” means that the other company has more than 20% of voting power in the associate company. |
| PRODUCER COMPANY | This is a company that is created by farmers/agriculturists which aim to help to improve the standard of living and ensure good support, incomes, and profitability. For example, the company Vanilla India Producer Company Limited is incorporated and the voting right of such companies is “One Man One Vote” regardless of the shareholding of these companies. |
| DORMANT COMPANY | Certain companies are formed and registered under the CA to hold an asset or intellectual property, but there are no accounts transactions taking place in this company. Such companies can make an application to the Registrar for obtaining the status of a dormant company. A dormant company is an excellent opportunity to start a company for a future project or hold an asset/intellectual property without having significant accounting transactions* On the other hand, if a company has not filed its annual returns for two consecutive years then such a company will also be called as a dormant company. The core policy of dormant companies is “Invest now, shine later”. The longer you exist the greater you are valued. As a dormant company, the company may not be active however, it still has the status of a company in the eyes of law. |
3. HOW TO REGISTER A COMPANY IN INDIA?
What is MCA21?

MCA21 is an e-Governance initiative by the Ministry of Company Affairs (MCA), Government of India. MCA21 enables easy and secure access of the MCA services to the corporate entities, professionals and citizens of India.
The MCA21 application is designed to fully automate enforcement and compliance of the legal requirements Companies Act, 2013 and Limited Liability Partnership community to meet their statutory obligations.
The MCA21 application is available to use for all MCA related services, which can be easily accessed over the Internet by corporate entities and professionals, and citizens of India.
Provisions of the MCA21 application :
1) Enables the business community to register a company and file statutory documents quickly and easily.
2) Provides easy access to public documents.
3) Helps faster and effective resolution of public grievances.
4) Helps registration and verification of charges easily.
5) Ensures proactive and effective compliance with relevant laws and corporate governance.
6) Enables the MCA employees to deliver best of breed services.
What are the steps involved in registering a company?
While the process would be based on the type of company you are registering, the general steps involved are :
Log on to www.mca.gov.in

To operate the MCA website, you first need to have a user profile. If you are a new user, click on register.

If you are an existing user, click on login, type in your credentials on the login page and click on “sign in”.

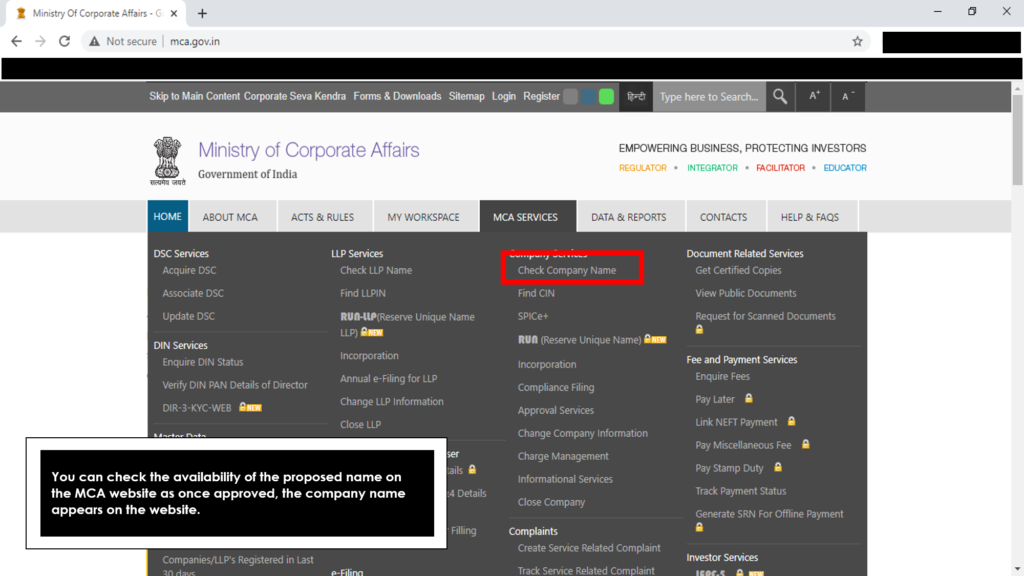
- Checking the Company Name Availability
- Acquiring a Director Identification Number (DIN)
- Acquiring a Digital Signature Certificate
- Obtaining an Incorporation Certificate
- Creating a Company Seal for official documentation
- Stamping of all Company Documents
- Acquiring a Permanent Account Number (PAN)
- Acquiring a Tax Account Number (TAN)
- Obtaining a certificate from the State/Municipal Inspector under the Shops and Establishment Act
- Applying for GST Registration
- Obtaining a Profession Tax Certificate from the State Profession Tax Office
- Completing a National Employees’ Provident Fund Registration
Dear readers. Hope you got answers to your questions. If you need any help, please feel free to connect. Let us know your thoughts in the comment section below.




